Could 'pausing' cell death be the final frontier in medicine on Earth and beyond?
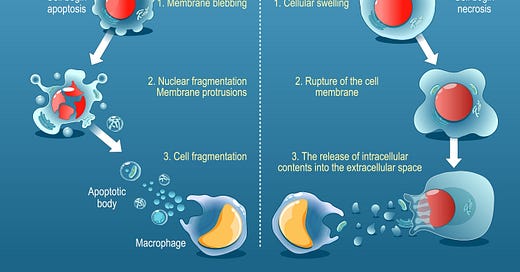
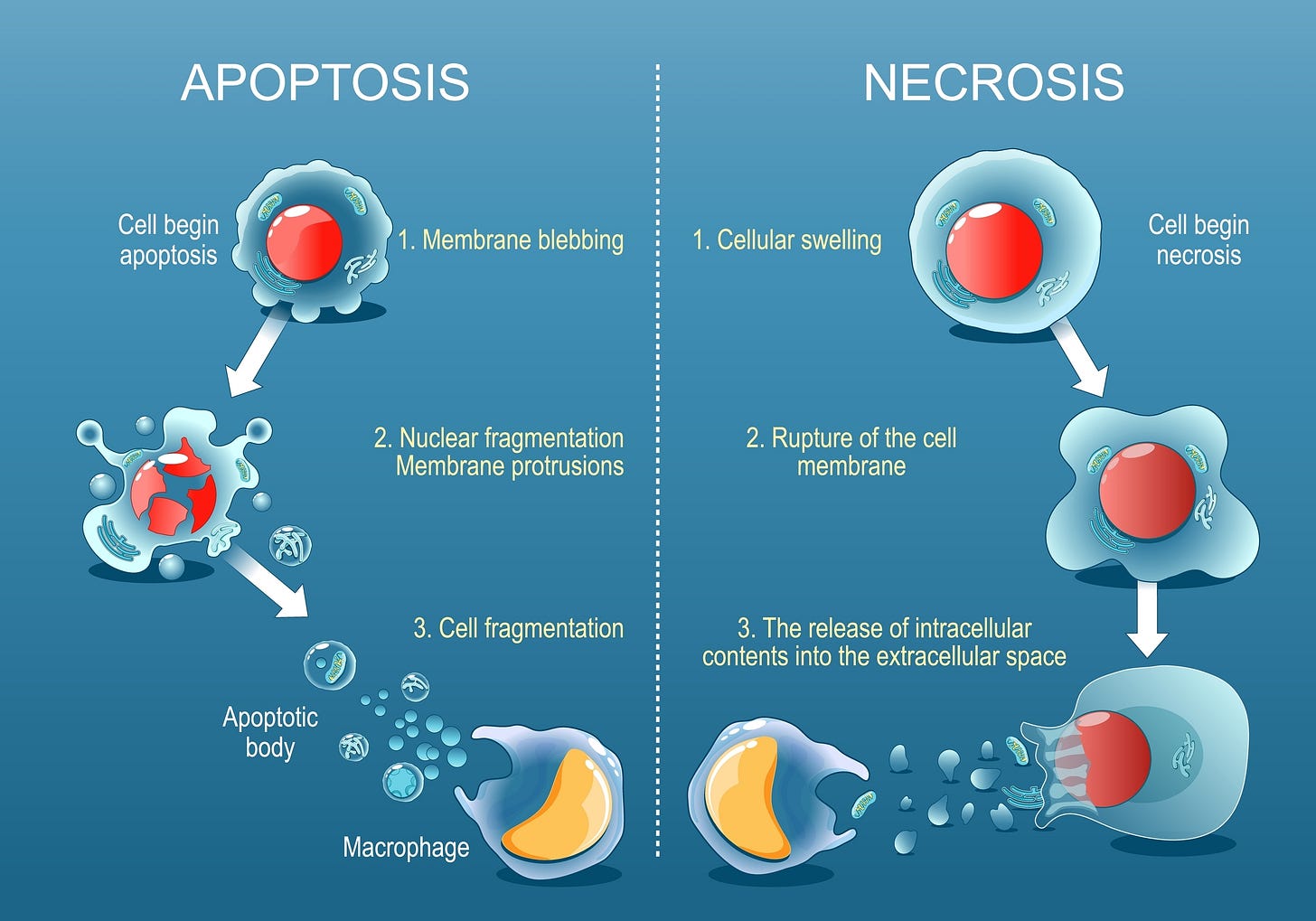
The process of necrosis, a form of cell death, may represent one of the most promising ways to change the course of human aging, disease and even space travel, according to a new study.
Love what you’re reading?
We’re growing fast and it’s all thanks to readers like you!
Our mission is simple: make the latest research news free and accessible to everyone. We don’t charge fees, and we never will.
If you believe in keeping knowledge open to all, you can support us with a donation:
Every contribution helps us stay free and independent. Thank you for being part of the ScienceDaily community!
Engineers develop self-healing muscle for robots
Single-atom catalysts change spin state when boosted by a magnetic field
Researchers proposed a novel strategy for using a magnetic field to boost the efficiency of single-atom catalysts -- thus speeding up helpful reactions used for ammonia production and wastewater treatment.
Scientists discover new evidence of intermediate-mass black holes
A series of studies sheds light on the origins and characteristics of intermediate-mass black holes.
Predicting underwater landslides before they strike
A new method for predicting underwater landslides may improve the resilience of offshore facilities.
Researchers present new experimental and theoretical results for the bound electron g-factor in lithium-like tin which has a much higher nuclear charge than any previous measurement. The experimental accuracy reached a level of 0.5 parts per billion. Using an enhanced interelectronic QED method, the theoretical prediction for the g-factor reached a precision of 6 parts per billion.
Does outdoor air pollution affect indoor air quality? It could depend on buildings' HVAC
Researchers determined how much outdoor particulate pollution affects indoor air quality. Their study concluded pollution from inversion and dust events is kept out of buildings, but wildfire smoke can sneak inside if efficient 'air-side economizers' are in use.
New quantum visualization technique to identify materials for next generation quantum computing
Scientists have developed a powerful new tool for finding the next generation of materials needed for large-scale, fault-tolerant quantum computing. The significant breakthrough means that, for the first time, researchers have found a way to determine once and for all whether a material can effectively be used in certain quantum computing microchips.
An iron oxide 'oxygen sponge' for efficient thermochemical hydrogen production
As the world shifts toward sustainable energy sources, 'green hydrogen' - hydrogen produced without emitting carbon - has emerged as a leading candidate for clean power. Scientists have now developed a new iron-based catalyst that more than doubles the conversion efficiency of thermochemical green hydrogen production.
Machine learning algorithm brings long-read sequencing to the clinic
SAVANA uses a machine learning algorithm to identify cancer-specific structural variations and copy number aberrations in long-read DNA sequencing data. The complex structure of cancer genomes means that standard analysis tools give false-positive results, leading to erroneous clinical interpretations of tumour biology. SAVANA significantly reduces such errors. SAVANA offers rapid and reliable genomic analysis to better analyse clinical samples, thereby informing cancer diagnosis and therapeutic interventions.
EV battery recycling key to future lithium supplies
Lightweight, powerful lithium-ion batteries are crucial for the transition to electric vehicles, and global demand for lithium is set to grow rapidly over the next 25 years. A new analysis looks at how new mining operations and battery recycling could meet that demand. Recycling could play a big role in easing supply constraints, the researchers found.
Waste to foundation: Transforming construction waste into high-performance material
In a major advancement for sustainable construction, scientists have created a cement-free soil solidifier from industrial waste. By combining Siding Cut Powder and activated by Earth Silica, an alkaline stimulant from recycled glass, scientists produced a high-performance material that meets compressive strength standards exceeding the 160 kN/m construction-grade threshold and eliminates arsenic leaching through calcium hydroxide stabilization. The technology reduces landfill volumes and carbon emissions, offering a circular solution for infrastructure development worldwide.
Unlocking precise composition analysis of nanomedicines
Current regulations for nanomedicines overlook the effects of the different forms of the same element, such as ions, nanoparticles, and aggregates. In a recent study, researchers developed a new analytical method combining an asymmetric flow field-flow fractionation system and mass spectrometry to separately quantify these forms. This technique allows for better quality control and safety evaluation of metal-based nanomedicines, promoting their development and clinical use, with applications also extending to food, cosmetics, and the environment.
Researchers have demonstrated a new technique that uses lasers to create ceramics that can withstand ultra-high temperatures, with applications ranging from nuclear power technologies to spacecraft and jet exhaust systems. The technique can be used to create ceramic coatings, tiles or complex three-dimensional structures, which allows for increased versatility when engineering new devices and technologies.
Portable sensor enables community lead detection in tap water
Lead contamination in municipal water sources is a consistent threat to public health. Ingesting even tiny amounts of lead can harm the human brain and nervous system -- especially in young children. To empower people to detect lead contamination in their own homes, a team of researchers developed an accessible, handheld water-testing system called the E-Tongue. This device was tested through a citizen science project across four Massachusetts towns.
The future of AI regulation: Why leashes are better than guardrails
Electronic tattoo gauges mental strain
Researchers gave participants face tattoos that can track when their brain is working too hard. The study introduces a non-permanent wireless forehead e-tattoo that decodes brainwaves to measure mental strain without bulky headgear. This technology may help track the mental workload of workers like air traffic controllers and truck drivers, whose lapses in focus can have serious consequences.
Traditional diagnostic decision support systems outperform generative AI for diagnosing disease
Researchers compared their long-standing diagnostic decision support systems AI tool, DXplain, with modern large language models like ChatGPT and Gemini, finding DXplain performed slightly better. They say their findings suggest that combining DXplain with LLMs could enhance clinical diagnosis and improve both technologies.
Thousands of sensors reveal 3D structure of earthquake-triggered sound waves
Earthquakes create ripple effects in Earth's upper atmosphere that can disrupt satellite communications and navigation systems we rely on. Scientists have now used Japan's extensive network of Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) receivers to create the first 3D images of atmospheric disturbances caused by the 2024 Noto Peninsula Earthquake. Their results show sound wave disturbance patterns in unique 3D detail and provide new insights into how earthquakes generate these waves.
A cheap and easy potential solution for lowering carbon emissions in maritime shipping
Reducing travel speeds and using an intelligent queuing system at busy ports can reduce greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from oceangoing container vessels by 16-24%, according to researchers. Not only would those relatively simple interventions reduce emissions from a major, direct source of greenhouse gases, the technology to implement these measures already exists.
Horses 'mane' inspiration for new generation of social robots
Interactive robots should not just be passive companions, but active partners -- like therapy horses who respond to human emotion -- say researchers.
Study deepens understanding of cell migration, important for potential medical advances
A new study integrated mathematical modeling with advanced imaging to discover that the physical shape of the fruit fly egg chamber, combined with chemical signals, significantly influences how cells move. Cell migration is critical in wound healing, immune responses, and cancer metastasis, so the work has potential to advance a range of medical treatments.
Groundwork laid for designer hybrid 2D materials
Materials scientists have succeeded in creating a genuine 2D hybrid material called glaphene.
Mid-air transformation helps flying, rolling robot to transition smoothly
Engineers have developed a real-life Transformer that has the 'brains' to morph in midair, allowing the drone-like robot to smoothly roll away and begin its ground operations without pause. The increased agility and robustness of such robots could be particularly useful for commercial delivery systems and robotic explorers.
New method provides the key to accessing proteins in ancient human remains
A new method could soon unlock the vast repository of biological information held in the proteins of ancient soft tissues. The findings could open up a new era for palaeobiological discovery.
Five things to do in virtual reality -- and five to avoid
A review of experimental research reveals how VR is best used and why it's struggled to become a megahit with consumers.
AI meets game theory: How language models perform in human-like social scenarios
Large language models (LLMs) -- the advanced AI behind tools like ChatGPT -- are increasingly integrated into daily life, assisting with tasks such as writing emails, answering questions, and even supporting healthcare decisions. But can these models collaborate with others in the same way humans do? Can they understand social situations, make compromises, or establish trust? A new study reveals that while today's AI is smart, it still has much to learn about social intelligence.
In nature's math, freedoms are fundamental
Scientists have developed a unified theory for mathematical parameters known as gauge freedoms. Their new formulas will allow researchers to interpret research results much faster and with greater confidence. The development could prove fundamental for future efforts in agriculture, drug discovery, and beyond.
New 2D quantum sensor breakthrough offers new opportunities for magnetic field detection
Physicists have unveiled a breakthrough in quantum sensing by demonstrating a 2D material as a versatile platform for next-generation nanoscale vectorial magnetometry.
Researchers engineer a herpes virus to turn on T cells for immunotherapy
A team identified herpes virus saimiri, which infects the T cells of squirrel monkeys, as a source of proteins that activate pathways in T cells that are needed to promote T cell survival.
New AI tool reveals single-cell structure of chromosomes -- in 3D
In a major leap forward for genetic and biomedical research, scientists have developed a powerful new artificial intelligence tool that can predict the 3D shape of chromosomes inside individual cells -- helping researchers gain a new view of how our genes work.
Ongoing surface modification on Jupiter's moon Europa uncovered
A series of experiments support spectral data recently collected by the James Webb Space Telescope that found evidence that the icy surface of Jupiter's moon Europa is constantly changing. Europa's surface ice is crystallizing at different rates in different places, which could point to a complex mix of external processes and geologic activity affecting the surface.
Observing one-dimensional anyons: Exotic quasiparticles in the coldest corners of the universe
Scientists have observed anyons -- quasiparticles that differ from the familiar fermions and bosons -- in a one-dimensional quantum system for the first time. The results may contribute to a better understanding of quantum matter and its potential applications.
Cosmic mystery deepens as astronomers find object flashing in both radio waves and X-rays
A team of international astronomers have discovered a new cosmic object emitting both radio waves and x-rays.
Solitonic superfluorescence paves way for high-temperature quantum materials
A new study in Nature describes both the mechanism and the material conditions necessary for superfluorescence at high temperature.
New chiral photonic device combines light manipulation with memory
Engineers have developed a multifunctional, reconfigurable component for an optical computing system that could be a game changer in electronics.
Electric buses struggle in the cold, researchers find
Researchers have released new insights on a pilot program involving all-electric buses in Ithaca, NY, USA -- with implications for cities, schools and other groups that are considering the electrification of their fleets, as well as operators, policymakers and manufacturers.
Cryogenic hydrogen storage and delivery system for next-generation aircraft
Researchers have designed a liquid hydrogen storage and delivery system that could help make zero-emission aviation a reality. Their work outlines a scalable, integrated system that addresses several engineering challenges at once by enabling hydrogen to be used as a clean fuel and also as a built-in cooling medium for critical power systems aboard electric-powered aircraft.
Just add iron: Researchers develop a clever way to remove forever chemicals from water
Researchers find that iron powder, an inexpensive alternative to activated carbon, does a better job at filtering PFOS from water -- it's 26 times more effective.
Cryo-em freezes the funk: How scientists visualized a pungent protein
Most people have witnessed -- or rather smelled -- when a protein enzyme called sulfite reductase works its magic. This enzyme catalyzes the chemical reduction of sulfite to hydrogen sulfide. Hydrogen sulfide is the rotten egg smell that can occur when organic matter decays and is frequently associated with sewage treatment facilities and landfills. But scientists have not been able to capture a visual image of the enzyme's structure until now, thus limiting their full understanding of how it works.
Hitting the right notes to play music by ear
A team analyzed a range of YouTube videos that focused on learning music by ear and identified four simple ways music learning technology can better aid prospective musicians -- helping people improve recall while listening, limiting playback to small chunks, identifying musical subsequences to memorize, and replaying notes indefinitely.
Nature-inspired breakthrough enables subatomic ferroelectric memory
A research team has discovered ferroelectric phenomena occurring at a subatomic scale in the natural mineral Brownmillerite.
Home water-use app improves water conservation
A new study has found that a smartphone app that tracks household water use and alerts users to leaks or excessive consumption offers a promising tool for helping California water agencies meet state-mandated conservation goals. The study found that use of the app -- called Dropcountr -- reduced average household water use by 6%, with even greater savings among the highest water users.
Machine learning simplifies industrial laser processes
Laser-based metal processing enables the automated and precise production of complex components, whether for the automotive industry or for medicine. However, conventional methods require time- and resource-consuming preparations. Researchers are now using machine learning to make laser processes more precise, more cost-effective and more efficient.
The magic of light: Dozens of images hidden in a single screen
New technology that uses light's color and spin to display multiple images.
A chip with natural blood vessels
Miniature organs on a chip could allow us to do scientific studies with great precision, without having to resort to animal testing. The main problem, however, is that artificial tissue needs blood vessels, and they are very hard to create. Now, new technology has been developed to create reproducible blood vessels using high-precision laser pulses. Tissue has been created that acts like natural tissue.
'Raindrops in the Sun's corona': New adaptive optics shows stunning details of our star's atmosphere
Scientists have produced the finest images of the Sun's corona to date. To make these high-resolution images and movies, the team developed a new 'coronal adaptive optics' system that removes blur from images caused by the Earth's atmosphere. Their ground-breaking results pave the way for deeper insight into coronal heating, solar eruptions, and space weather, and open an opportunity for new discoveries in the Sun's atmosphere.
How brain stimulation alleviates symptoms of Parkinson's disease
Persons with Parkinson's disease increasingly lose their mobility over time and are eventually unable to walk. Hope for these patients rests on deep brain stimulation, also known as a brain pacemaker. In a current study, researchers investigated whether and how stimulation of a certain region of the brain can have a positive impact on ambulatory ability and provide patients with higher quality of life. To do this, the researchers used a technique in which the nerve cells are activated and deactivated via light.
Emotional responses crucial to attitudes about self-driving cars
When it comes to public attitudes toward using self-driving cars, understanding how the vehicles work is important -- but so are less obvious characteristics like feelings of excitement or pleasure and a belief in technology's social benefits.
New fuel cell could enable electric aviation
Engineers developed a fuel cell that offers more than three times as much energy per pound compared to lithium-ion batteries. Powered by a reaction between sodium metal and air, the device could be lightweight enough to enable the electrification of airplanes, trucks, or ships.



“Researchers find that iron powder, an inexpensive alternative to activated carbon, does a better job at filtering PFOS from water -- it's 26 times more effective.”
This could actually be super useful. Hopefully those involved in industries with PFOS can notice that there are alternatives like this.