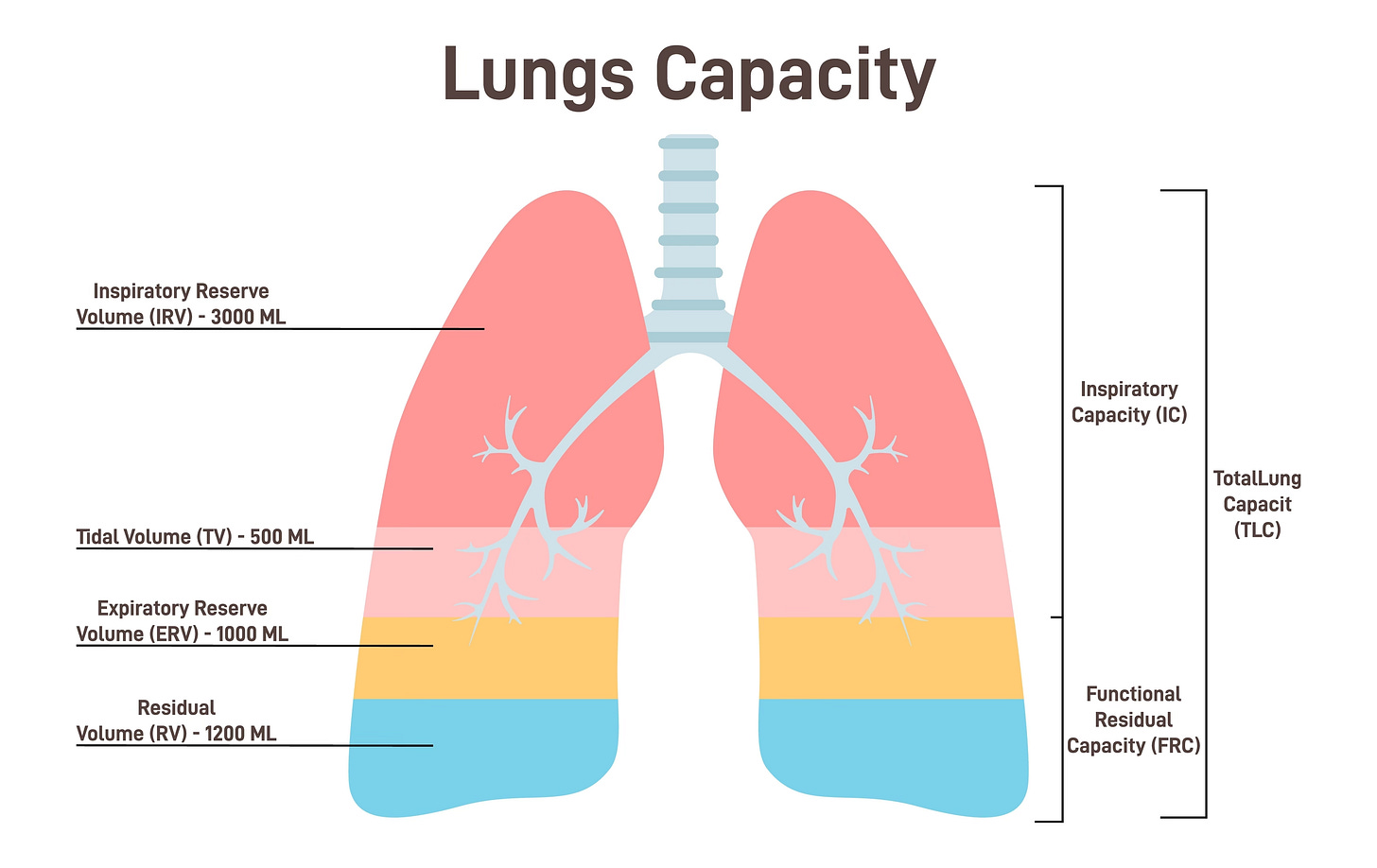
New scan method unveils lung function secrets
A new method of scanning lungs is able to show in real time how air moves in and out of the lungs as people take a breath in patients with asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and patients who have received a lung transplant. It enables experts to see the functioning of transplanted lungs and could enable medics to identify sooner any decline in lung function.
Image: inspiring.team/Shutterstock.com
Scientists discover a 'Goldilocks' zone for DNA organization, opening new doors for drug development
In a discovery that could redefine how we understand cellular resilience and adaptability, scientists have unlocked the secret interactions between a primordial inorganic polymer of phosphate known as polyphosphate (polyP), and two basic building blocks of life: DNA and the element magnesium. These components formed clusters of tiny liquid droplets -- also known as condensates -- with flexible and adaptable structures.
Virus that threatened humanity opens the future
Scientists have developed an innovative therapeutic platform by mimicking the intricate structures of viruses using artificial intelligence (AI).
New drug to prevent migraine may start working right away
A drug recently approved to prevent migraine may start working right away, according to a new study. The study looked at the drug atogepant, which is a calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) receptor antagonist taken by mouth.
Gene editing tool reduces Alzheimer's plaque precursor in mice
A new gene editing tool that helps cellular machinery skip parts of genes responsible for diseases has been applied to reduce the formation of amyloid-beta plaque precursors in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease, researchers report.
Propranolol reduces tremors in Parkinson's disease
The standard medication levodopa does not always work against tremors in Parkinson's disease, especially in stressful situations. Propranolol, however, does work during stress, providing insight into the role of the stress system in tremors. MRI scans reveal that propranolol directly inhibits activity in the brain circuit that controls tremors. Doctors may consider this medication when levodopa is ineffective.
Public shows greater acceptance of RSV vaccine as vaccine hesitancy appears to have plateaued
A year after becoming available, vaccines to protect against RSV in newborns and older adults are being more widely accepted by the American public, according to a new health survey.
Foundational technology to make cancer cells revert to normal cells?
A research team has developed a groundbreaking technology that can treat colon cancer by converting cancer cells into a state resembling normal colon cells without killing them, thus avoiding side effects.
Researchers develop tool to fast-track measurement of protein interactions for drug discovery
Researchers have created a platform, called SIMPL2, that revolutionizes the study of protein-protein interactions by simplifying detection while improving measurement accuracy. While protein-protein interactions have previously been considered 'undruggable' using small molecules, the platform addresses this challenge by facilitating the measurement of these interactions -- improving our understanding of the types of molecules needed to control them.
New research identifies key cellular mechanism driving Alzheimer's disease
Researchers have unveiled a critical mechanism that links cellular stress in the brain to the progression of Alzheimer's disease (AD). The study highlights microglia, the brain's primary immune cells, as central players in both the protective and harmful responses associated with the disease.
Hospitals that have adopted the Center for Medicare and Medicaid (CMS) 'hospital-at-home' program, which serves as an alternative to admission to brick-and-mortar facilities, are concentrated in large, urban, not-for-profit, and academic hospitals, highlighting need for targeted incentives to expand program to smaller, rural, and non-teaching hospitals.
Brain map clarifies neuronal connectivity behind motor function
Scientists traced connectivity between neurons to identify how the brain communicates with the spinal cord to control motor function.
Researchers find compromised indoor air in homes following Marshall Fire
A new study finds gases harmful to human health lingered for weeks following the fire.
Three years after the Dec. 30, 2021, Marshall Fire destroyed more than 1,000 homes in Boulder County, two new studies offer insight into what happens to air quality and health in the aftermath of urban wildfires.
Unraveling the power and influence of language
A choice was made to include each word in this sentence. Every message, even the most mundane, is crafted with a specific frame in mind that impacts how the message is perceived. The study of framing effects is a multidisciplinary line of research that investigates when, how, and why language influences those who receive a message and how it impacts their response.
Can the heart heal itself? New study says it can
Physician-scientists found that a subset of artificial heart patients can regenerate heart muscle, which may open the door to new ways to treat and perhaps someday cure heart failure.
Microscopic discovery in cancer cells could have a big impact
Scientists have uncovered new details about the mechanism behind cancer progression. Researchers explored the influence the mechanical stiffening of the tumor cell's environment may have on the structure and function of the nucleus.
Research points the way to lifesaving antiparasitic drugs while unlocking a scientific mystery
A breakthrough in understanding how a single-cell parasite makes ergosterol (its version of cholesterol) could lead to more effective drugs for human leishmaniasis, a parasitic disease that afflicts about 1 million people and kills about 30,000 people around the world every year.
Researchers discover replication hubs for human norovirus
Combining bioinformatics and experimetal approaches, researchers have discovered replication hubs for human norovirus, the leading cause of viral gastroenteritis accounting for an estimated 685 million cases and approximately 212,000 deaths globally per year. The findings could lead to designing antiviral drugs to prevent, control or treat these serious infections.
A tropical disease in Switzerland: Call for coordinated action on Chagas disease
Researchers conducted a comprehensive review of Chagas disease in Switzerland. Although typically found in Latin America, Chagas disease affects between 2,000 and 4,000 people in Switzerland. The review underscores the need for improved screening and healthcare strategies to eliminate Chagas disease in Switzerland.
AI may help researchers with medical chart review, study finds
Researchers trained a large language model to read medical charts, looking for signs that kids with ADHD received the right follow-up care when using new medications.
Poor vascular health accelerates brain aging
Using an AI tool, researchers have analyzed brain images from 70-year-olds and estimated their brains' biological age. They found that factors detrimental to vascular health, such as inflammation and high glucose levels, are associated with an older-looking brain, while healthy lifestyles were linked to brains with a younger appearance.
Breakthrough study set to change how osteosarcomas are diagnosed and treated
Researchers have been able to identify at least three distinct subtypes of a rare type of bone cancer for the first time, which could transform clinical trials and patient care.
AI may help researchers with medical chart review
Researchers trained a large language model to read medical charts, looking for signs that kids with ADHD received the right follow-up care when using new medications.
Integrating GABA and dopamine signals to regulate meal initiation
When you are feeling hungry, the brain takes the necessary steps toward consuming a meal. Many of these steps are not well known, but a new study reveals brain circuits and chemical messengers that contribute to the regulation of meal initiation and food intake. The findings have implications for the development of improved therapies to manage obesity, a worldwide epidemic.
New findings point to an opportunity to improve therapies that use small RNAs to silence disease-causing genes, potentially including those involved in cancer.
Getting rehab earlier improves concussion outcomes
People who suffer from continued symptoms of concussion should seek a referral to physical therapy as soon as possible, new research suggests.
Potential culprit identified in lingering Crohn's disease symptoms
A study may explain why some patients with Crohn's disease continue to experience symptoms, even in the absence of inflammation.
A research team examined the atomic composition of enamel samples from two human teeth.
Patience isn't a virtue; it's a coping mechanism
Impatience, studies of more than 1,200 people found, is the emotion people feel when they face a delay that seems unfair, unreasonable, or inappropriate -- like a traffic jam outside of rush hour, or a meeting that should have ended 15 minutes ago. Patience is the form of emotion regulation we use to cope with those feelings of impatience.
New molecule-creation method a 'powerful tool' to accelerate drug synthesis and discovery
A team of chemists has unveiled a novel method to simplify the synthesis of piperidines, a key structural component in many pharmaceuticals. The study combines biocatalytic carbon-hydrogen oxidation and radical cross-coupling, offering a streamlined and cost-effective approach to create complex, three-dimensional molecules. This innovation could help accelerate drug discovery and enhance the efficiency of medicinal chemistry.
Machine psychology: A bridge to general AI?
Artificial intelligence that is as intelligent as humans may become possible thanks to psychological learning models, combined with certain types of AI.
Brain inflammation alters behavior according to sex, mouse study finds
Inflammation in the hippocampus -- the brain's memory center -- significantly alters motivation and behavior in mice, according to new research.
Charting a path toward overcoming glioblastoma resistance to chemotherapy
Mutational signatures etched into the cells' genome by an anti-cancer drug called temozolomide (TMZ) uncover an Achilles' heel for TMZ chemotherapy resistance, according to new research.
Shiitake-derived functional food shows suppression of liver fibrosis progression
A research team found out how AHCC, a standardized extract of cultured Lentinula edodes mycelia, might be able to suppress the progression of liver fibrosis.
Antibodies can improve the rehabilitation of people with acute spinal cord injury. Researchers have investigated this with promising results. For the first time, it was possible to identify patient groups that displayed a clinically relevant treatment effect.
Scientists make surprising discovery pinpointing when good cholesterol becomes harmful
Researchers have discovered that certain components of so-called 'good' cholesterol -- high-density lipoproteins (HDL) -- may be associated with an increased prevalence of cardiovascular disease.
Molecular gardening: New enzymes discovered for protein modification pruning
Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein modifications made from the protein ubiquitin, and thereby regulate proteins. Malfunctioning of DUBs could lead to diseases, including cancer and neurodegenerative disorders. A protein called USP53 has been recently linked with progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis, a hereditary liver disease in children, yet its mechanism of action has remained elusive. While its sequence made it part of a deubiquitinase family, previous attempt to detect catalytic activity had remained inconclusive. Now, a team has decoded the mode of action of USP53 and its related enzyme called USP54.
A user manual for yeast's genetic switches
When introducing genes into yeast to make it produce drugs and other useful substances, it is also necessary to reliably switch the production on or off. Researchers have found three gene regulation design principles that provide a flexible guideline for the effective control of microbiological production.
Study finds slowing of age-related declines in older adults
A new study reveals significant improvements in the health of older adults when compared to previous generations.
Breakthrough study reveals how assisted reproduction affects placenta and child's growth
Researchers have studied placental genes to explore how Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART) affects a child's development. Differences showed up between pregnancies from frozen and fresh embryo transfers in the placentas. Changes were also observed in the function of a gene associated with obesity and type 2 diabetes.
Tinkering with the 'clockwork' mechanisms of life
Opening new doors for the development of nanotechnologies in medicine and other fields, scientists recreate and compare two natural mechanisms to better program the timescale of molecular communication and functionality.
MRI-first strategy for prostate cancer detection proves to be safe, study finds
There are several strategies for the early detection of prostate cancer. The first step is often a blood test for prostate-specific antigen (PSA). If PSA levels exceed a certain threshold, the next step typically involves taking a tissue sample for analysis. Another option is to use magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to search for signs of a tumor before deciding whether a biopsy is necessary, reserving biopsies only for cases where abnormalities are detected. Researchers at conducted a study to determine whether this MRI-first approach is safe over the long term. Their findings show that this strategy poses no additional risk to patients for at least three years.
Effect of somatosensory electrical stimulation on hand choice
Hand choice, an unconscious decision, is influenced by target-related information, but if these are non-informative, the choice will be approximately 50-50. In this equilibrium situation, non-target information may also aid in decision-making, but no research has demonstrated this. Now, researchers have investigated the effect of somatosensory stimulation on motor decisions in healthy participants. The results revealed that wrist stimulation significantly increased the likelihood of choosing the stimulated hand, highlighting its application in stroke rehabilitation.
The surprising role of gut infection in Alzheimer's disease
Researchers have discovered a surprising link between a chronic gut infection caused by a common virus and the development of Alzheimer's disease in a subset of people. It is believed most humans are exposed to this virus -- called cytomegalovirus or HCMV -- during the first few decades of life. According to the new research, in some people, the virus may linger in an active state in the gut, where it may travel to the brain via the vagus nerve -- a critical information highway that connects the gut and brain. Once there, the virus can change the immune system and contribute to other changes associated with Alzheimer's disease. This virus may be a target for antiviral treatments.
Genes linked to deadly parasites' spread beyond Africa identified
Parasites that cause the deadly illness known as sleeping sickness can spread beyond their native Africa as a result of mutations to key genes, a study shows.
How to deal with narcissists at home and at work
The best way to deal with narcissistic people in your personal life may be the hardest advice to take, according to an expert who has studied narcissism for more than 20 years. The best course of action is to identify narcissistic people early on and get them out of your life, said the professor of psychology.
This prototype sunscreen protects your skin and cools you off, too
Wearing sunscreen is important to protect your skin from the harmful effects of UV radiation but doesn't cool people off. However, a new formula protects against both UV light and heat from the sun using radiative cooling. The prototype sunblock kept human skin up to 11 degrees Fahrenheit (6 degrees Celsius) cooler than bare skin, or around 6 degrees Fahrenheit (3 degrees Celsius) cooler than existing sunscreens.
Developmental disorder discovery could lead to better treatments for Rett syndrome
New discoveries about the severe developmental disorder known as Rett syndrome could open the door to better treatments for the devastating, life-shortening condition.
Study links alcohol consumption to more severe nut allergy reaction
Findings of a new study into severe allergic reactions offer a sobering warning to people allergic to tree nuts and, more broadly, could lead to quicker diagnoses in emergency care for people with all anaphylactic allergies.
New 'molecular flipbook' gives researchers the best look yet at ribosomal motion
A team of researchers used a new technique, called high-resolution template matching, or HRTM, to uncover in unprecedented detail the movement of ribosomes -- the molecular structures that synthesize proteins inside cells.
Genetic discovery links new gene to autism spectrum disorder
New research has identified previously unknown genetic links to autism spectrum disorder (ASD), providing new insights into the genetic underpinnings of the condition.
Delivery timing in mothers with chronic hypertension
Physician researchers found 39 weeks of gestation is optimal for delivery in mothers with chronic hypertension.
First successful clinical trial of VU319 brings Alzheimer's treatment one step closer
Phase I clinical trial of a drug was successfully completed, with promise to treat Alzheimer's and other neurodegenerative diseases. The compound, named VU319, is the first end-to-end drug discovery effort related to memory loss, starting from the earliest basic science research through human clinical trials.
Researchers have combined two sequencing technologies in single cells to find new differences in mRNAs resulting from Alzheimer's disease, dementia with Lewy bodies and Parkinson's disease.
How a new gut microbe drives the gut-lung axis
A team has discovered a new communication pathway between the gut and lung. Their findings highlight how a little-known member of the gut microbiome reshapes the lung immune environment to have both beneficial and detrimental effects on respiratory health.
Drinking coffee may help prevent mental decline in people with atrial fibrillation
A study of more than 2,400 people with atrial fibrillation, who had an average age of 73, found that drinking more than five cups of caffeinated coffee daily was associated with better performance on an array of cognitive tests than drinking less than one cup or avoiding coffee altogether.
Researchers have uncovered important insights that could improve how mental health conditions are treated with brain stimulation therapy -- a treatment where electrical signals are used to stimulate specific parts of the brain.
Research shows how music can reduce distress
A new study has demonstrated for the first time how and why music can reduce distress and agitation for people with advanced dementia. The study involved interviews with staff and music therapists on inpatient mental health dementia wards, a review of published research, and a national survey of UK healthcare professionals.
Scientists design workaround that improves response to flu vaccine
Stitching together four molecules found in the standard flu vaccine ensures an immune response to all of them, scientists have shown.