ScienceDaily: All - September 04, 2024
Today's top research news
Assorted, distinctive behavior of molten uranium salt revealed by neutrons
New research addresses the fundamental science necessary to increase the efficiency of nuclear energy. Researchers have now documented the unique chemistry dynamics and structure of high-temperature liquid uranium trichloride salt, a potential nuclear fuel source for next-generation reactors.
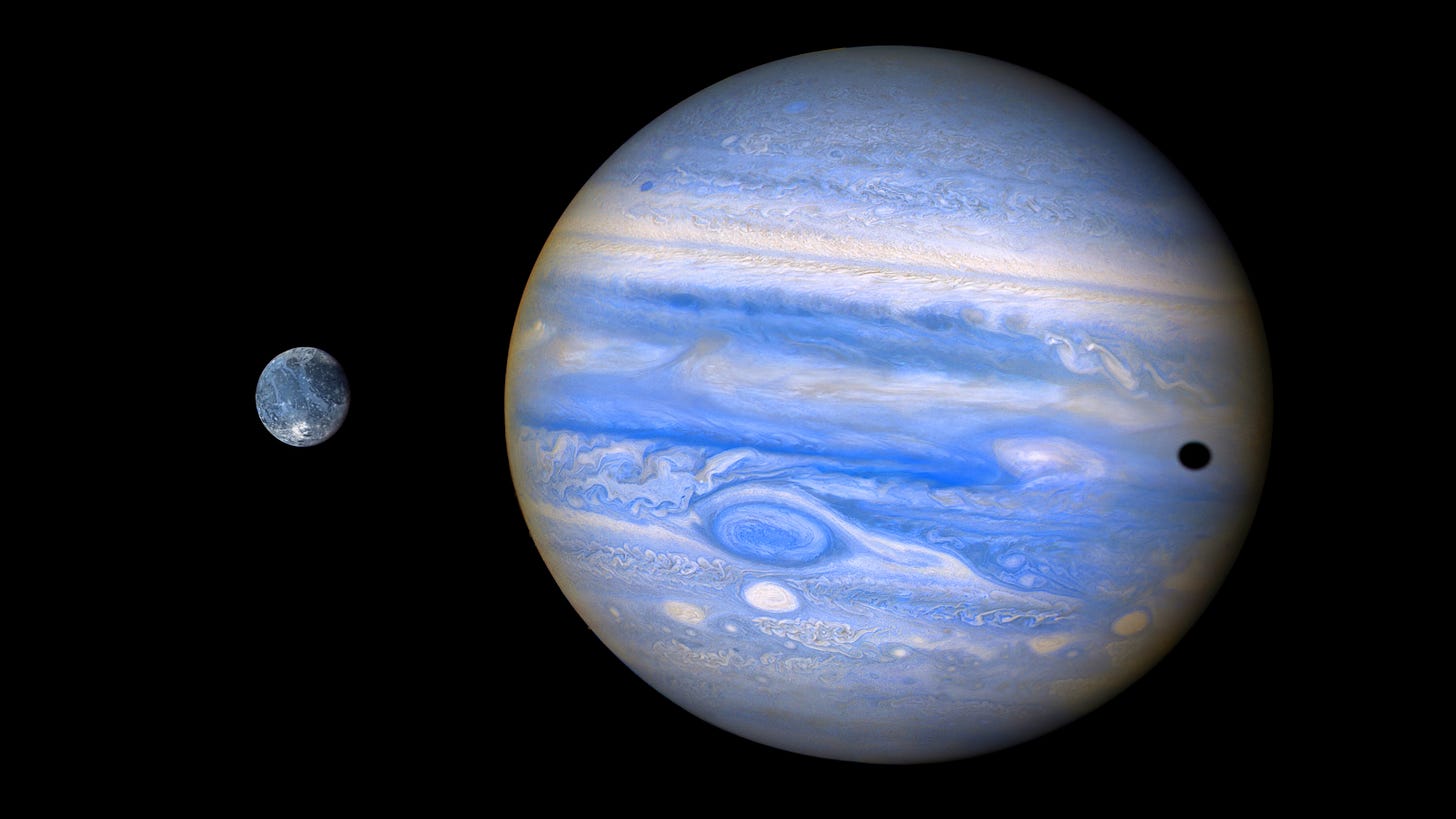
Gigantic asteroid impact shifted the axis of Solar System's biggest moon
Around 4 billion years ago, an asteroid hit the Jupiter moon Ganymede. Now, a researcher realized that the Solar System's biggest moon's axis has shifted as a result of the impact, which confirmed that the asteroid was around 20 times larger than the one that ended the age of the dinosaurs on Earth, and caused one of the biggest impacts with clear traces in the Solar System.
Image: Claudio Caridi/Shutterstock.com
How bright is the universe's glow? Study offers best measurement yet
Over billions of years, the universe's stars and galaxies shined their light into space, leaving behind an imperceptibly faint night light known as the cosmic optical background. NASA's New Horizons spacecraft has traveled to the edge of Earth's solar system and captured the most accurate measurement of this glow to date.
Infertility challenges amongst endangered wild songbird population revealed in new study
A groundbreaking study has provided the most comprehensive estimate to date of infertility rates in a threatened wild animal species.
Ketamine clinics vary widely in pregnancy-related safeguards
With ketamine for depression & PTSD growing rapidly in use, but with concerns about potential impact on a fetus, a study shows wide variation in pregnancy testing & contraception guidance at clinics offering IV and nasal spray treatment.
Heart failure during pregnancy is a dangerous and often under-detected condition because common symptoms -- shortness of breath, extreme fatigue and trouble breathing while lying down -- are easily mistaken for typical pregnancy discomforts. A new study showed an artificial intelligence (AI)-enabled digital stethoscope helped doctors identify twice as many cases of heart failure compared to a control group that received usual obstetric care and screening.
A double twist makes cracking easier to resist
Additive manufacturing, precision robotics and architected design markedly increase crack resistance in concrete.
50-year generation gap in Minnesota's longest-lived fish
The bigmouth buffalo is a fish that's native to Minnesota and known for its longevity. Researchers wanted to find out more about the species, especially how they migrate, spawn, and how often their offspring live into adulthood.
New approach can help detect and predict mental health symptoms in teens
The majority of mental health disorders manifest during adolescence and relate to a multiplex interplay of neurobiological and environmental factors. Instead of considering these factors in isolation, a newly developed manifold learning technique can model brain-environmental interactions, which vastly improves detection of existing mental health symptoms and prediction of future ones compared to current methods. The study underscores the importance of considering the adolescent brain in conjunction with the environment in which it develops.
Researchers have discovered that inflammation in the gut leaves long-term marks on intestinal stem cells (ISCs) that reduce their ability to heal the intestine, even after inflammation has receded. This is important because it affects ISCs' response to future challenges.
Scientists identify potential new immune system target to head off the spread of breast cancer cells
In a study using human breast cancer cells, scientists say they have potentially identified immune system white blood cells that appear to be the closest neighbors of breast cancer cells that are likely to spread. The researchers say the finding, focused on a white blood cell called a macrophage, may provide a new biological target for immunotherapies designed to destroy spreading cancer cells that are often markers for worsening disease.
Unveiling the molecular mechanisms linking aging with neurodegenerative diseases
Aging is a major risk factor for neurodegenerative diseases, but the molecular mechanisms behind this relationship are not clear. In a recent study, researchers explored the role of PQBP3, a protein that helps stabilize the nuclear membrane, in cellular senescence and neurodegeneration. Their findings suggest that PQBP3 might be a promising therapeutic target for managing neurodegenerative diseases and the neuronal symptoms of aging.
Keep devices out of bed for better sleep
Despite what we've been led to believe, the timing of evening screen use, rather than the activity itself, negatively impacts youth sleep, a new study has found.
From cavities to sleep apnea: Dentists can assume new role in saving lives
New research reveals how dental check-ups could be the first line of defense against deadly sleep disorders.
Researchers develop tool that measures health of a person's gut microbiome
A team of researchers has developed an innovative computational tool that analyzes the gut microbiome, a complex ecosystem of trillions of bacteria, fungi, viruses and other microorganisms within the digestive system, to provide insights into overall well-being.
Researchers give adult zebra finches back their ability to learn new songs
We all know the adage, 'You can't teach an old dog new tricks.' As we age, our ability to learn new skills, like mastering a foreign language or picking up a musical instrument, seems to fade. The culprit? A decline in brain plasticity - the brain's capacity to rewire itself and adapt to new challenges. But what if we could rewind the clock on this age-related decline? A new study offers a tantalizing glimpse into this possibility.
Rein tension may affect horse behavior
High rein tension was found to be associated with trotters opening their mouths, which indicates pain or discomfort in the mouth.
Open wide: Human mouth bacteria reproduce through rare form of cell division
New research has uncovered an extraordinary mechanism of cell division in Corynebacterium matruchotii, one of the most common bacteria living in dental plaque. The filamentous bacterium doesn't just divide, it splits into multiple cells at once, a rare process called multiple fission.
False-positive mammograms discourage some women from future screenings
A false-positive mammogram may deter women from future screenings, according to a new study. But staying on schedule remains key to early detection of cancer.