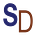Toward new targeted treatments for rheumatoid arthritis
New research may lead to new targeted treatments for rheumatoid arthritis (RA), an autoimmune disease that causes joint inflammation and destruction.
airdone/shutterstock.com
Cultural artifacts serve as 'cognitive fossils,' helping uncover the psychology of the past
No two societies in history think exactly alike. In fact, the mindset of a given society throughout history can help historians unpack important clues about the effects of psychological shifts -- such as more social trust or more openness. Researchers explain how modern computing methods like text mining, face detection algorithms, and melodic extraction programs can enable large-scale analysis of cultural artifacts such as paintings, stories, or clothing to uncover this psychological data.
Yeast with an over half synthetic genome is created in the lab
Researchers have combined over seven synthetic chromosomes that were made in the lab into a single yeast cell, resulting in a strain with more than 50% synthetic DNA that survives and replicates similarly to wild yeast strains. A global consortium is working to develop the first synthetic eukaryote genome from scratch. The team has now synthesized and debugged all sixteen yeast chromosomes.
Scientists have engineered a chromosome entirely from scratch that will contribute to the production of the world's first synthetic yeast.
Scientists take major step towards completing the world's first synthetic yeast
A team of Scientists has completed construction of a synthetic chromosome as part of a major international project to build the world's first synthetic yeast genome. The work represents completion of one of the 16 chromosomes of the yeast genome, which is part of the biggest project ever in synthetic biology; the international synthetic yeast genome collaboration. The collaboration, known as 'Sc2.0' has been a 15-year project involving teams from around the world (UK, US, China, Singapore, UK, France and Australia), working together to make synthetic versions of all of yeast's chromosomes. Alongside this paper, another 9 publications are also released today from other teams describing their synthetic chromosomes. The final completion of the genome project -- the largest synthetic genome ever -- is expected next year.
New antifungal molecule kills fungi without toxicity in human cells, mice
A new antifungal molecule, devised by tweaking the structure of prominent antifungal drug Amphotericin B, has the potential to harness the drug's power against fungal infections while doing away with its toxicity, researchers report.
Physicists trap electrons in a 3D crystal
Physicists have trapped electrons in a pure crystal, marking the first achievement of an electronic flat band in a three-dimensional material. The results provide a new way for scientists to explore rare electronic states in 3D materials.
Scaling up nano for sustainable manufacturing
A research team has developed a high-performance coating material that self-assembles from 2D nanosheets, and which could significantly extend the shelf life of electronics, energy storage devices, health & safety products, and more. The researchers are the first to successfully scale up nanomaterial synthesis into useful materials for manufacturing and commercial applications.
How the antioxidant glutathione keeps mitochondria healthy
Scientists have discovered how mitochondria sense and control their glutathione levels, an antioxidant produced throughout the body. The first nutrient-sensing mechanism identified for an organelle, the finding has great translational potential.
Some unexpected shark strandings and subsequent surprises following autopsies have, ironically, taken marine biologists millions of years back in time as they look to the future with concern. Adding chapters to an evolutionary tale involving the infamous megalodon shark (the 'Meg'), they think their work suggests there are more warm-blooded sharks out there than previously believed, and -- based on the Meg's demise -- these species may be at great risk from warming seas.