Bella moths use poison to attract mates: Scientists are closer to finding out how
Researchers sequence the bella moth genome, which they used to pinpoint specific genes that may confer immunity to noxious alkaloids.
AI tool creates 'synthetic' images of cells for enhanced microscopy analysis
Researchers have developed a method to use an image generation AI model to create realistic images of single cells, which are then used as 'synthetic data' to train an AI model to better carry out single-cell segmentation.
World's oases threatened by desertification, even as humans expand them
Oases are important habitats and water sources for dryland regions, sustaining 10% of the world's population despite taking up about 1.5% of land area. But in many places, climate change and anthropogenic activities threaten oases' fragile existence. New research shows how the world's oases have grown and shrunk over the past 25 years as water availability patterns changed and desertification encroaches on these wet refuges.
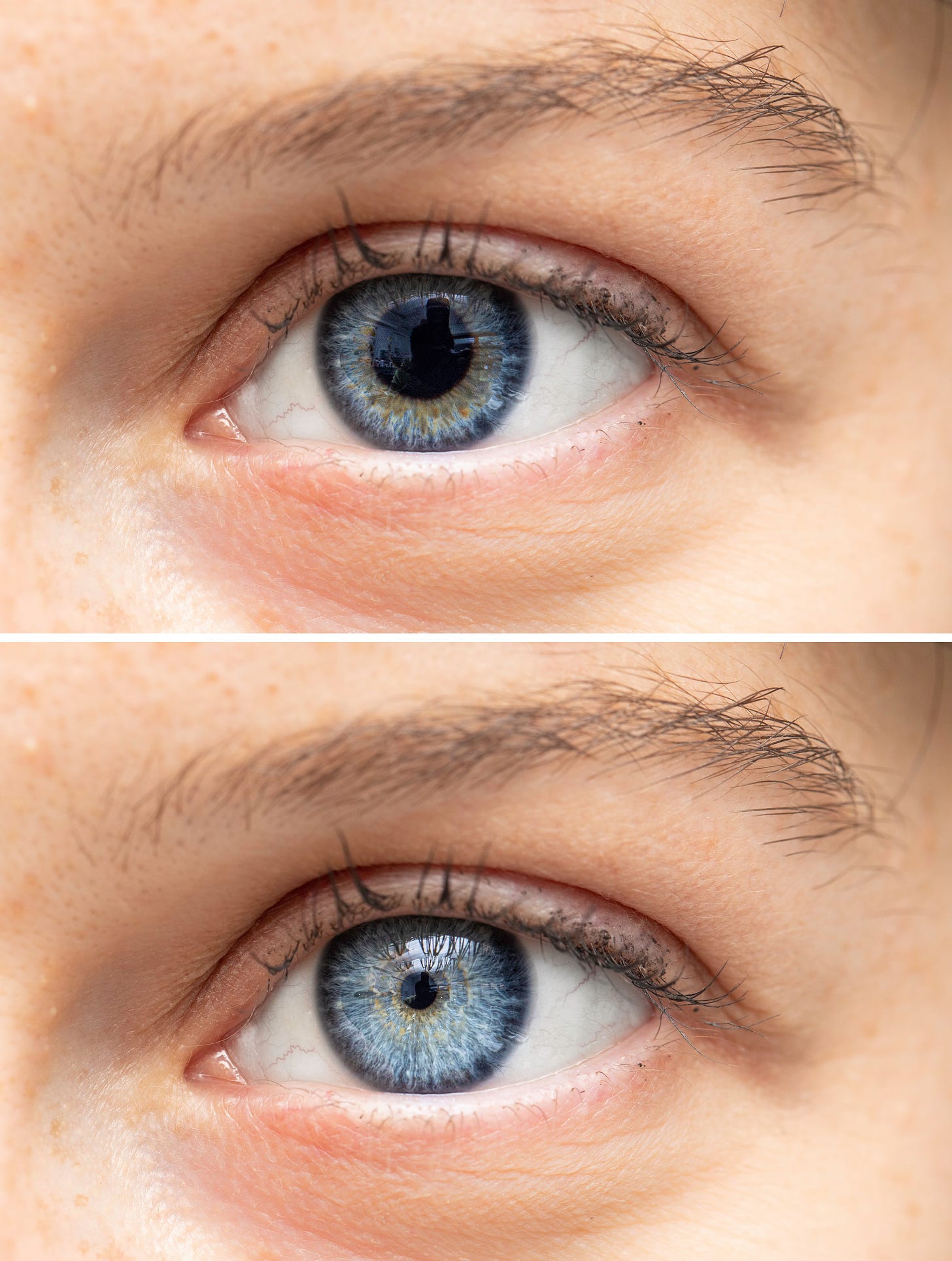
Eye-opener: Pupils enlarge when people focus on tasks
Normally, a person's pupils naturally widen (or dilate) in low-light environments to allow more light into the eye. However, in a new study, researchers reported that a person's pupils also dilate when they are concentrating on tasks. In particular, they found that the more a person's eyes dilated during the task, the better they did on tests measuring their working memory.
Image: enlarged and small pupils, sruilk/Shutterstock.com
Liquid droplets shape how cells respond to change
New research has shown that cells regulate cAMP/PKA signaling by forming liquid droplets that segregate excess PKA catalytic subunits where they can do no harm. Some cancers may block the formation of liquid droplets, leading to hyperactive signaling and tumor formation.
Life goals and their changes drive success
Though life goals change over time, a study of teen goals indicates that goals of education and high prestige can drive success.
Researchers have uncovered a remarkable metal alloy that won t crack at extreme temperatures due to kinking, or bending, of crystals in the alloy at the atomic level. Unlike most materials, the new alloy keeps its shape and resists cracking at both high and low temperature extremes, making it potentially suitable for demanding applications like high-efficiency aerospace engines.
To find life in the universe, look to deadly Venus
Despite surface temperatures hot enough to melt lead, lava-spewing volcanoes, and puffy clouds of sulfuric acid, uninhabitable Venus offers vital lessons about the potential for life on other planets, a new paper argues.
Everest mountaineer's letters digitized
Letters written by the famous mountaineer George Mallory have been made available to a global audience for the first time, in the centenary year of his fatal attempt to scale Everest.
Giant galactic explosion exposes galaxy pollution in action
Astronomers have produced the first high-resolution map of a massive explosion in a nearby galaxy, providing important clues on how the space between galaxies is polluted with chemical elements.
2D materials rotate light polarization
Physicists have shown that ultra-thin two-dimensional materials such as tungsten diselenide can rotate the polarization of visible light by several degrees at certain wavelengths under small magnetic fields suitable for use on chips.
Simulated microgravity affects sleep and physiological rhythms
Simulated effects of microgravity significantly affect rhythmicity and sleep in humans, a new study finds. Such disturbances could negatively affect the physiology and performance of astronauts in space.
Genetically engineering a treatment for incurable brain tumors
Scientists are developing and validating a patent-pending novel immunotherapy to be used against glioblastoma brain tumors. Glioblastomas are almost always lethal with a median survival time of 14 months. Traditional methods used against other cancers, like chemotherapy and immunotherapy, are often ineffective on glioblastoma.
Social programs save millions of lives, especially in times of crisis
Primary health care, conditional cash transfers and social pensions have prevented 1.4 million deaths of all ages in Brazil over the past two decades, according to a new study. If expanded, these programs could avert an additional 1.3 million deaths and 6.6 million hospitalizations by 2030.
AI and physics combine to reveal the 3D structure of a flare erupting around a black hole
Based on radio telescope data and models of black hole physics, a team has used neural networks to reconstruct a 3D image that shows how explosive flare-ups in the disk of gas around our supermassive black hole might look.
Invasive species sound off about impending ecosystem changes
Anticipating changes to ecosystems is often at best an educated guess, but what if there was a way to better tune into possible changes occurring? Researchers have discovered that the silent growth of non-native invasive plants can affect the soundscape of an ecosystem. These altered soundscapes, the acoustic patterns of a landscape through space and time, may provide a key to better observing the hard-to-see physical and biological changes occurring in an ecosystem as they are beginning.